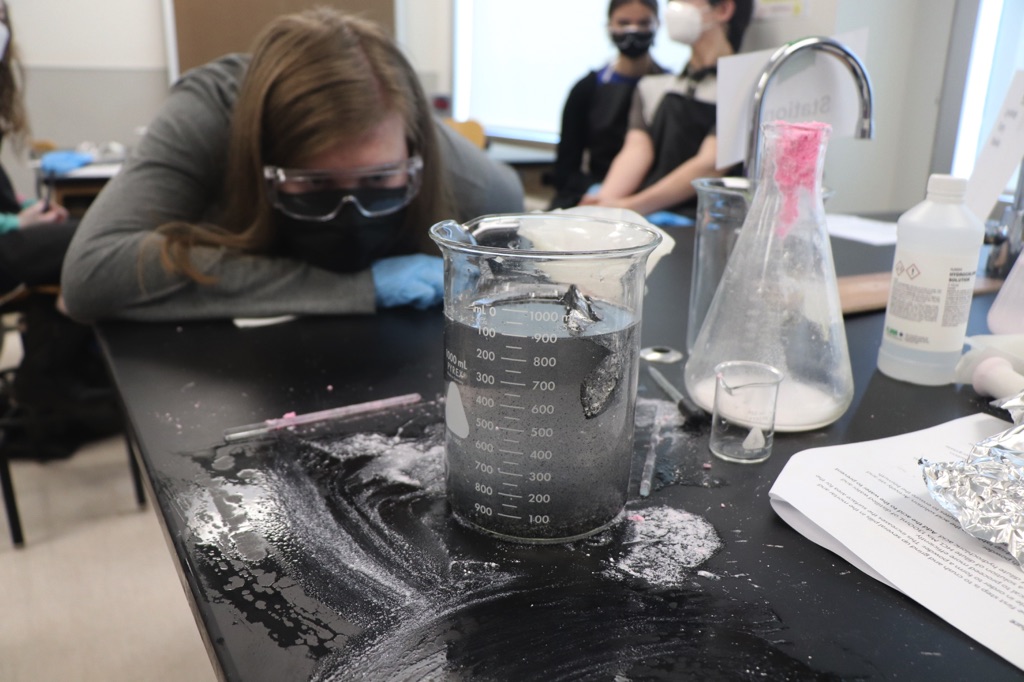
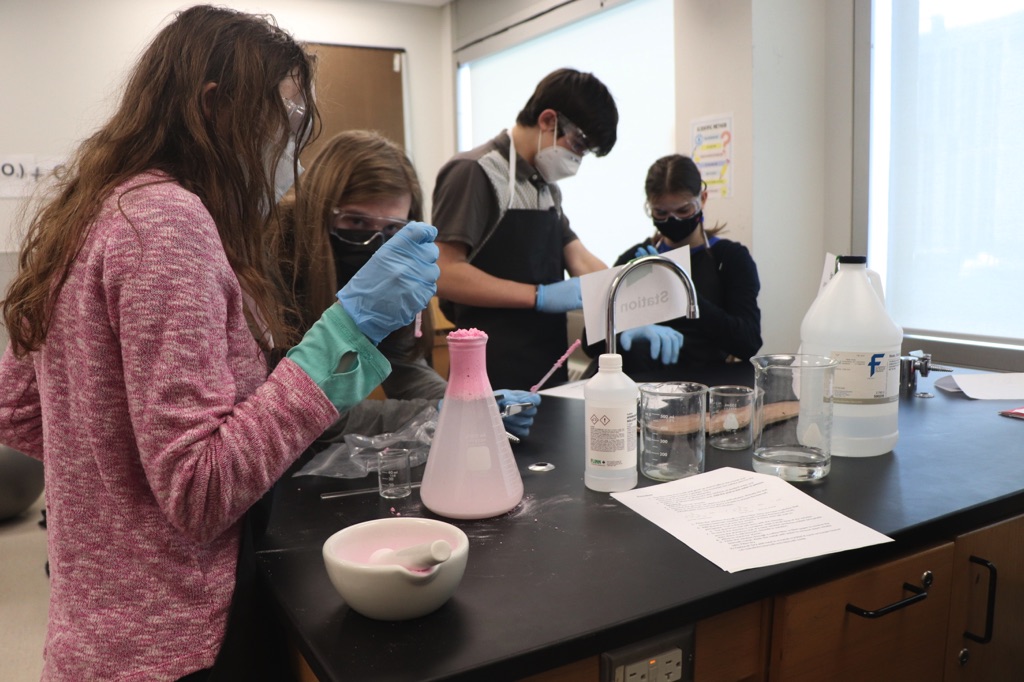
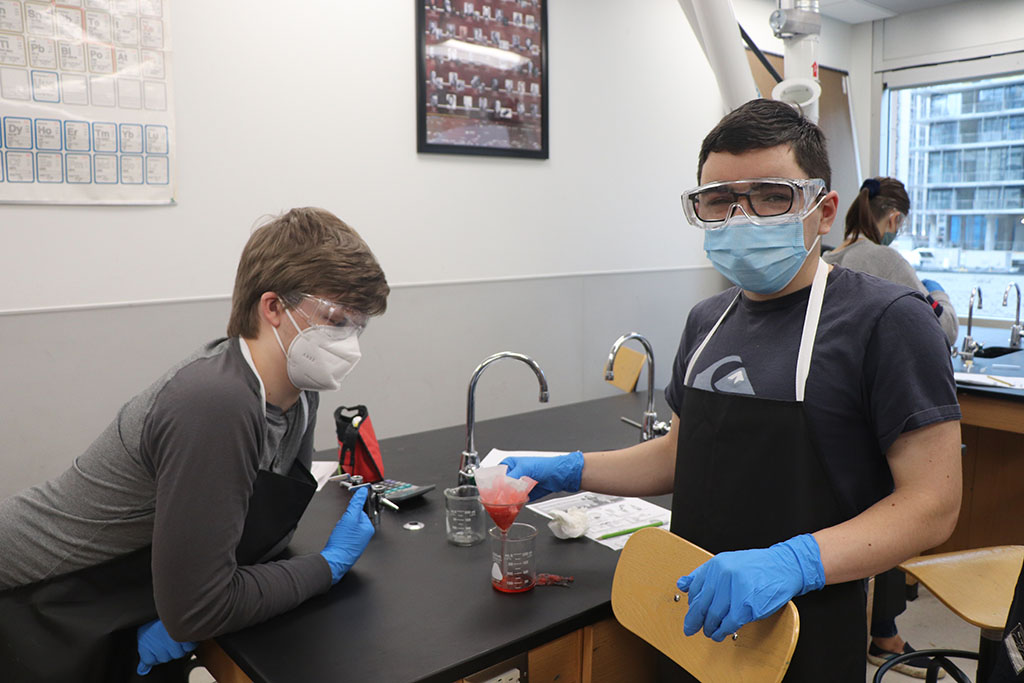
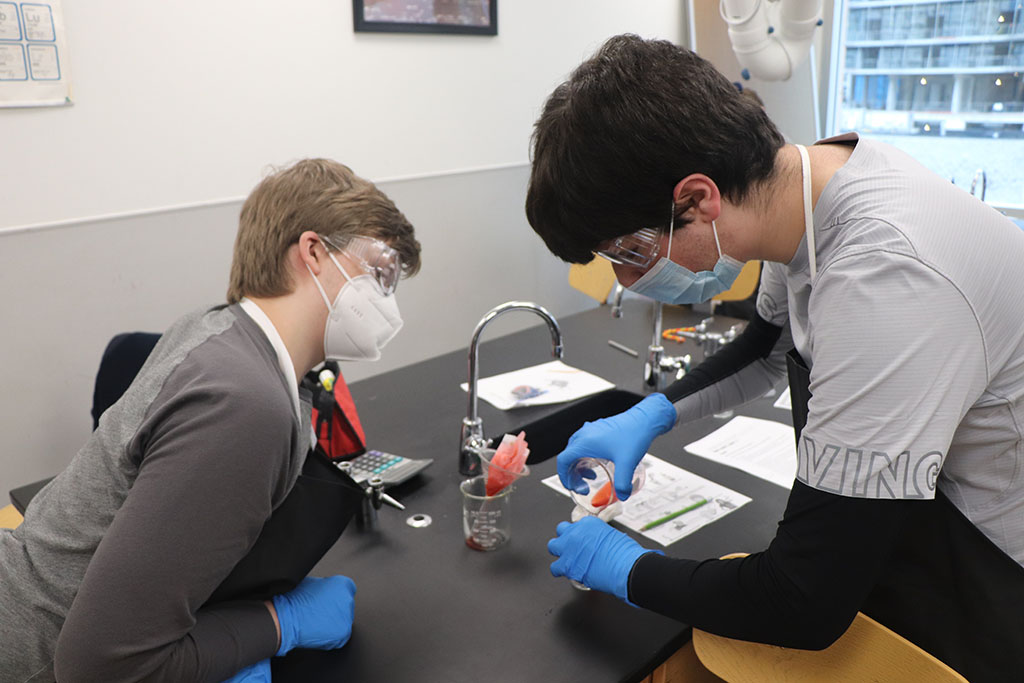
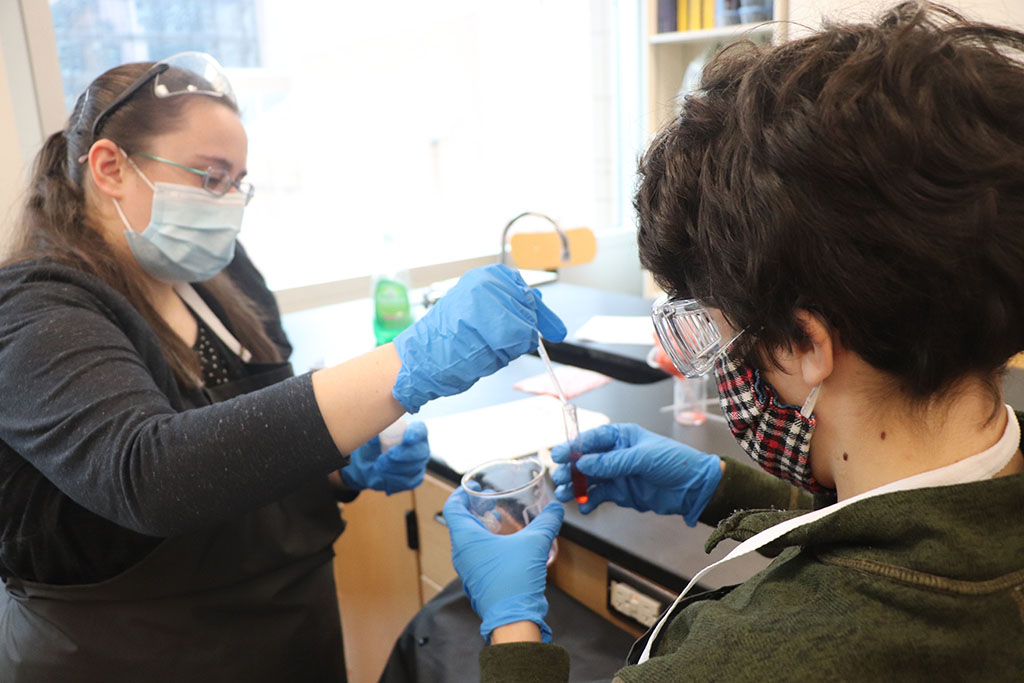
The students actively extracted bismuth metal from pepto bismol tablets. A soft metal that has similar properties to lead, pepto bismol is widely used in medicine and cosmetics though does not have a specific medical purpose! Bismuth actually helps with the absorption of fluid across the intestinal wall!
To isolate the Bismuth metal, the students combined Pepto Bismol and HCl (hydrochloric acid). Students then filtered the solution. Student then pondered: “Hmmm… we have bismuth chloride…” We put aluminum in the solution to form Aluminum chloride allowing the Bismuth to precipitate out of solution. The students watched in incredible amazement as the Bismuth formed immediately as these little black dots in solution! We filtered and fired the bismuth sample. The students extracted 3.2g of bismuth from 96 Pepto Bismol tablets.
WoW! One student shared that this was a great experiment!
The students asked careful questions throughout as they extracted a solid from a solution. Incredible!
We got to extract an element!
We experimented with stomach medication
We turned a medication into an element!
We did science!